Books flyer
/Books for Sale, downloadable flyer to share
Click on the heading topic to see articles/blog posts on that topic. Click the specific articles on sub topics below. A * (star asterisk) indicates the article/blog post contains a free download tip sheet or worksheet.
General Behavior
Function of behavior: why is the child doing this
Sensory or Behavior?
123 Magic/Not Listening to Directions
Error Correction
Consequences and Discipline
“If I have to tell you one more time!”
Environmental/Physical problems that cause behavior
Pick your battles!
Sensory or Behavior, Sensory overview
Feelings by Age
Specific Behaviors
Aggression
When your child says “I Hate you!”
Attention-Seeking behaviors
Feeding problems
Whining
Lying
Cursing
Arguing
Disrespect/Backtalk
Sleep problems
Potty training, Encropresis(soiling) behavior, Bed Wetting, Potty Training: readiness, tips, strategies
Behavior Charts
First/Then chart
Rewards and Consequences
Angry Birds reward chart
Volume Management chart
Keep Working slider
Traffic light behavior chart
Autism
Social Skills for Autism/Aspergers
Matching activity to teach focus, “Put in” activities
Teaching Language skills
Morning Routines with Picture Schedules
Social Stories
Anxiety
Anxiety: tips for parents
Food allergies and anxiety
Shy, Sensory-Avoidant, Social Anxiety
Selective Mutism
Panic Attack Advice*
Coping Strategies List*
OCD or not
Breathing Exercises for children *
Breathing exercises for strong emotions
Starting at a new school
Separation Anxiety
Anxiety about going new places
ODD (Oppositional Defiant Disorder)
ODD tips for parents
Depression
Positive Self-Talk
Depression in Young Children: signs and symptoms
Depression Coping Strategies
Anger
Emotionality/Meltdowns Tips for parents
Anger Management
Coping Strategies List*
Breathing exercises*
“Frozen” theme coping strategies
ADHD
ADHD tips for parents
ADHD tips for teachers
Using a Fidget, Fidgets for Focus
Matching activities to teach focus to preschoolers
Morning Routines with Picture Schedules
Timers
Executive Functioning
Executive Functioning explanation
Goal Setting, Goal Worksheet *
Autism
Social Skills for Autism/Aspergers
Matching activity to teach focus, “Put in” activities
Teaching Language skills
Morning Routines with Picture Schedules
Social Stories
Social Skills
Making Friends at a New School
Bullying: How to help, Bullying, or not?, Tattling or Telling?
Losing a Game
Social Skills for Autism/Aspergers
Social stories
Communication
Getting Kids to Talk
Communicating with teens and children
Communication picture game
Teaching Language skills
Communication and Following Directions ‘Barrier’ games
College/Jobs
College Choices
College Application steps for teens
Finding a job tips for teens and young adults
School
When your child hates writing*
Pencil problems tips
Using a Fidget tool, Fidgets for Focus
Homework organizer worksheet *
Homework Battles
Starting at a new school
Family Issues
Siblings messing with each others things
Sibling of a child with special needs*
Sibling Fights*
Homework Battles
Boredom problems, Bored List *, Local Activities *
Parenting Issues
Screen Time
Teaching Kids to be Grateful
Appropriate Sexual Development in Children
Mom tribe
Getting on the same page (parents/coparents)
Divorced Coparenting tips (and worksheet for kids)*
Chores: suggestions per age
Your ‘job’ as a stay-at-home parent
You’re not a bad mom if…
What if the baby isn’t healthy?
Other
No Social Media/Feeling Left out
Medication for Mental Health/Behavior issues and Children
and more! (Use Search box or Scroll below)
Books for Sale, downloadable flyer to share


Sensory vs Behavior
By Patience Domowski, LCSW
How do I know if my child’s behavior is sensory-related or a behavioral problem? Parents wonder this all the time. The simple answer is that it's often hard to tell and sometimes the reasons overlap. Often the issues can be both.
Sensory issues are sensitivities related to the senses- see, hear, feel, taste, smell. People can be over-sensitive or under-sensitive to senses. Children can be sensory- seeking: they do certain things to get certain sensory stimulation, such as excessively rubbing a soft blanket, or sensory-avoidant: they do things to avoid sensations they cannot handle, such as covering their ears for loud sounds. Some behaviors that are sensory related can also be behaviors for other reasons, which makes this so difficult to figure out. Some children are both sensory seeking and sensory avoidant for different senses.
Some behaviors you might see in a sensory-seeking child: running around and crashing into furniture/items, desires tight hugs and squeezes often, chews/sucks on toys/fingers/etc, bites/scratches/squeezes people or furniture, likes to feel various items and objects, fabrics, textures. These behaviors are not to get something they want from another person, like a toy, or attention, but for sensory input into their body.
Some behaviors you might see in a sensory-avoidant child include: won’t touch or eat certain textures- wet or soft items often like pudding or yogurt, screams and covers ears/eyes in certain bright lights or loud noises (may seem normal lighting or sound to a non-sensory person however, but to a sensory kid it’s overwhelming), avoids certain fabrics/clothing.
If a child is screaming or running around, those are not obviously sensory related behaviors, so how do you know the difference? The way to figure it out is to try to figure out the function, or the WHY, of the behavior. Is the child running around because they are trying to get your attention? (Behavioral) Do they seem to be very hyper and struggle to sit still? (Could be Sensory) Is the child screaming to get what they want, get attention, or because other people are doing it? (Behavior) Or are they upset with no clear reason why? (Could be sensory) Would the child do the behavior if no one was in the room with them? One of the simpler ways to figure out if a behavior is for sensory purposes is if the behavior would occur without any other interaction from another person. If the child was alone in a room and would still do that behavior, it is likely sensory- because they are not trying to avoid something they don’t want to do, get attention, or get something from someone else (the other functions of behavior). [For more info on functions of behavior see my other article on this topic].
Many children do sensory-seeking behaviors that are not a major problem as most children like to run in circles, dance around, touch soft items, etc. because it feels good to them. It's only a sensory problem when the behaviors are disrupting the family or school setting, or causing distress or interference in the child’s life. To have your child diagnosed with a sensory disorder please seek an evaluation from an occupational Therapist (OT). OTs are available through Early Intervention (if your child is under age 5), the school system, or private agencies.
If the behavior is for any other reason than sensory-stimulation it's a behavioral issue, not a sensory issue. If a child is throwing a tantrum because they didn't get candy, that’s behavior. If they are melting down because the lights are too bright- that’s sensory. Sometimes it's hard to know why so trying to figure out when the behaviors occur, what set it off, and the environment is very helpful. If your child is verbal, ask them what the problem is if they can verbalize it. Sometimes taking data is helpful to see patterns and figure out what settings the behavior seems to occur in most often.
So what do we do about it? We want to treat the behavior differently based on the function (or WHY) of the behavior. If a child is screaming for attention purposes, we would likely want to ignore them and teach them a better way to get attention. But if the child is screaming to avoid a loud sound, we would want to help them protect their ears- such as providing headphones in noisy environments. If the child doesn't want to wear underwear to be difficult or in control that is much different than a child who is complaining the underwear is itchy. So once we figure out WHY the behavior is occurring, then we come up with a solution.
OTs help kids de-sensitize and meet their sensory needs in more appropriate ways. So a kid who cannot tolerate certain clothing would probably be brushed until they could tolerate it. They would have the child do sensory activities like jumping on a trampoline or crashing into cushions to meet those needs instead of grabbing people or running into walls. Behaviorally the child can be given rewards for making good choices- like using a sensory toy or strategy, such as biting a chew toy instead of mom’s arm. We want the child to meet their needs in an appropriate way or get them to a point that they don't need that problematic behavior anymore.
Often the behaviors are both sensory and behavioral and they can feed each other, so sometimes a combined approach to treatment is helpful. Many children with ADHD, autism, and anxiety also have sensory issues. However a child can have sensory issues without a mental health diagnosis as well. Try to have your child evaluated by both a behavioral/mental health therapist and an OT to figure out the right diagnosis as that will be very helpful in coming up with a treatment plan.
Because sensory and behavior needs vary so much per child, and figuring out the function can be difficult sometimes, it is important to meet with an experienced professional to help figure out a plan specifically for your child. OTs and Behavioral Specialists/Therapists are the best professionals for this. Some Physical Therapists (PTs) can be helpful as well. Not all child therapists are familiar with sensory issues however, so find someone who knows something about sensory concerns and behavior.

“If I have to tell you one more time!”
Reducing frequency of prompting
An Explanation of 123 Magic and Supernanny’s “warnings” techniques
by Patience Domowski, LCSW
Do you find yourself telling your child to do something (or stop doing something) a million times and they don’t listen? Do they ignore you until you really start to lose it and scream at them? Do you find yourself threatening things but nothing seems to work? Or are you always arguing with your child? Well here’s the secret solution!
To reduce telling children a “million” times to do something you need to have a specific consequence tied in as a result for not listening. So if the child isn’t doing what you’ve asked right away they learn they get something taken away and then they start learning to listen right away. The power is in the consequence. They might not care that you are frustrated, but they sure do care when you take away that ipad!
You may have heard of 123 Magic but don’t have time to read the book. I thought I’d summarize the strategy here. (Okay I’ll admit I haven’t read the book either, but I know the strategy!). Remember the “Magic” is in the consequence, not the words!
To use 123 Magic you give the direction and say “That’s One” to the child to let them know you told them what to do once. Wait a few seconds/minutes and if the child doesn’t comply you give the directive again and add “That’s Two”. After a minute if the child still refuses to comply then you say “That’s Three” and give them a consequence. Important note- 123 Magic is NOT counting to three. So it’s not “Pick up that toy, 1. 2. 3. Okay you’re in trouble now,” but rather giving the direction 3 times after 3 occasions of refusals.
Now before you start this you should prepare your child by explaining how it works (during a calm time, not in a moment of noncompliance). You should also have a go-to ideas of consequences in your head that you can use. It doesn’t always have to be the same consequence but it needs to be something the child cares about, and something that you are able to enforce/follow through with. Also don’t use a consequence that will punish yourself. Like taking away TV time when you know that’s the only time you can actually shower, for example!
Here’s how you can explain the new program to your child “Mom and Dad are tired of telling you MANY times to do things. It’s frustrating for us and then we yell at scream at you. I'm sure you don’t like when that happens either. So we’re going to use a new strategy. It’s called “123 Magic”. Isn’t that a cool name? Basically we will only tell you THREE times to do something and then you get a consequence. The consequence will be ____ (examples: lose a toy/go to room/loss of privilege/etc). So when we ask you to do something we will tell you “That’s one” so you know we told you the first time. If you don’t listen right away then we’ll remind you “that’s two” so you know this is the second time we asked you to do something. If we get to the third time we will see “that’s three” and you will have the consequence right away. You still have to do what we told you to do but you also get a consequence. If you do it before we get the Three then you don’t get the consequence.” Then practice it with something easy like throwing trash in the trash can or putting a toy in a box so the child gets in the habit of listening right away and understands how it works during a calm time/teaching time, not just waiting for a problem time.
After you’ve used this strategy a few times the child learns that they do not want to get to Three. They know you MEAN IT and you don’t have to scream at them. You just have to say “That’s three. Now you’ve lost ipad time tonight” in a calm tone. [Ignore any resulting screaming/crying and still insist the child completes the direction you gave them].
When you FIRST start using 123 Magic you might want to remind them of what they are going to lose. Here is an example for when you FIRST start using this system with a child who is refusing to follow directions.
Example “Pick up your jacket and hang it up. That’s one.” (wait a few seconds). “Remember if we get to 3 you don’t get to go out for ice cream with us tonight.” (wait a few seconds). “Pick up your jacket and hang it up. That’s two. If we get to three, you lose ice cream tonight.” (wait for compliance). “Okay this is 3. You lose ice cream tonight. You still need to pick up your jacket.”
After that there should be no more explanations. No more pleading. Nothing else. Just “That’s one” “That’s Two” “That’s Three”. You should NOT be saying “If I have to tell you again…” or “I’ve already told you x times” or explain why they need to listen, etc. Just give a simple direction with the numbers. Because they will know what the consequence is. Then take away the privilege or whatever the consequence is calmly and quietly.
Supernanny has a similar system where she calls it “Warnings”. It’s really the same thing. You can do it that way too. For example “Stop hitting your sister. That’s the First warning”. (behavior continues) “Stop hitting your sister. This is the 2nd warning.” (behavior continues). “This is the 3rd warning.” (wait briefly, if behavior continues then) “Okay that was 3 warnings- now no more computer time tonight.”
The “magic” is that there is no more arguing and parents don’t have to repeat themselves many times. Children soon learn to comply within 1-2 prompts instead of 20!
Check out the 123 Magic books program and read some articles by Supernanny as there are some great strategies there. Links are below.
Also see my "resources" page for links to more articles.
Reference:
http://www.123magic.com/1-2-3-magic
http://csgreeley.org/sites/default/files/files/1-2-3-magic.pdf


Arguing
Just like it takes two to tango, it takes two to argue. So when a parent says the child constantly argues they are implying that the parent is arguing back too. How do we stop this as parents? Simple answer: STOP ARGUING. Don’t answer back. Ignore constant invitations to engage in arguing behavior. Remind your child you already gave them a response and that’s it. If they continue to ask, perhaps give a consequence.
Arguing problem example
Child: Mom, may I have a cookie right now?
Mom: No, we are saving the cookies for dessert tonight.
Child: But mom, I’m really hungry! I want a cookie now!
Mom: No, you just had a snack. It’s almost dinner time.
Child: I’m still hungry! I can’t wait for dinner! I want it now!
Mom: I told you, you have to wait until dessert time after dinner.
Child: But I want it now! You never let me have anything to eat! You starve me all the time! You’re the worst mom ever!
Mom: No, I feed you all the time, We’re eating dinner in about 15 minutes anyway.
Child: (Starts to cry/tantrum) I want a cookie! I hate you!
Mom: (loses cool) What is your problem?! I’m the best mom ever- some moms never give their kids cookies! If you keep acting like this I’ll never feed you again!
… okay maybe not to that extreme… In this example the child engaged mom in arguing, even though Mom did a great job sticking to her word and not giving in to what the child wanted, the child still was arguing to get what they wanted and mom was losing her cool and getting upset.
Let’s try this instead. Sometimes its called “Asked and Answered” (I didn’t invent that term, but it makes a lot of sense. Basically you just remind the child you already gave them a response. You might explain why, if not obvious, but then you let it go.)
Arguing Solution:
Child: Mom, may I have a cookie right now?
Mom: No, we are saving the cookies for dessert tonight.
Child: But mom, I’m really hungry! I want a cookie now!
Mom: I already answered your question. I’m not going to talk to you any more about it.
Child: I want it now! I want a cookie! I can’t wait! I’m starving! You never feed me! Why can’t I have one now? (etc…)
Mom: (ignores child)
Argument over.
Child can continue to scream/tantrum but knows he’s not going to engage mom in discussing this anymore.
Sometimes if child does this kind of behavior a lot I would add this..
Mom: If you keep asking for a cookie/screaming/crying, then you won’t get a cookie after dinner for dessert at all. It’s your choice.
Hopefully child will stop at this point. If they don’t then mom needs to stick to her word and no cookie during dessert time. Next time the child will likely remember this consequence and avoid this behavior completely. It may take a few tries to get to that point!

Disrespect/Talking back
If your child has many difficult behaviors, including disrespect, I would recommend focusing on the other behaviors first. If your child is being disrespectful just to get a reaction from you, then just ignore it.
However if that is not the case, and when you are ready to focus on disrespect then try a few things:
-be respectful to your child (don’t call them mean names, belittle them, etc).
A lot of parents don’t realize that they are being disrespectful to their child. This doesn’t mean we treat child on same level authority-wise as adults, but think about would we talk to our friends or spouse the same way we address our kids? If we can talk nicer to them they will often respond nicer back.
-expect respect, and correct them by having them try again in a better way. You model/say what the child should say instead of what they did say and have them repeat it back. [See article on error correction]
-provide a consequence for constant disrespectful behavior [see article on consequences]
If disrespect continues then you might need to figure out what’s gone wrong with your relationship with your child/teen and work on that. In order for children to follow directions and be respectful, etc parents MUST have a good relationship with their child. Relationship is the MOST important thing!! Many teens will say their parents are mean to them or disrespectful so they refuse to listen to them. Or they feel their father (for example) doesn’t have a relationship with them so why would they listen to him. If you don’t have a good relationship with your child work on that relationship FIRST before expecting better behavior or more respectful responses.

Anxiety
For kids with severe anxiety I recommend therapy and possibly medication if they can’t get through the day or are having many panic attacks.
While the child might ask you multiple times about various anxious scenarios I would suggest not constantly talking about their sources of anxiety and constantly reassuring them, but instead refer them to a professional therapist. They often may only need a few sessions to start feeling better. They need some reassurances from parents that they are safe/okay, but constantly talking about it can lead to them thinking more about their worries instead of getting them to think about other relaxing thoughts. Don’t tell your child not to worry about things or make them feel bad for having anxiety- it’s not their fault and saying this will just make them feel worse. Help them examine evidence if their fears are irrational to challenge their anxious thoughts. Also ask them how to make them feel better and teach them how to solve their problems. Also help them develop some coping strategies.
Coping strategy suggestions:
· Take deep breaths from stomach (instead of chest)
· Picture a relaxing scene/favorite place (often kids pick a vacation, or thinking about their pet)
· Progressive musical relaxation (tighten and then relax your muscles)
· Try to change your thoughts by questioning your fears if they are really likely to happen. [For example- if you worry your parents will die, then think- is it really likely? Probably not if you examine the evidence- that they aren’t sick and have never died before. Then you can try to challenge your thought and remember they will likely be fine and you can try to relax].
· Problem solve: If your child is asking “What if” this or that happens, ask them to try to think of logical solutions.
Anxiety about going somewhere new
Some kids have a lot of anxiety about going somewhere new (or somewhere they haven't been in a while) or visiting/meeting new people. Some kids may not show their anxiety, but rather internalize it (may be worried but not express it) and other kids express it in different ways. Some kids show this anxiety in the typical way: clinging to mom/dad, crying, refusing to go. Other kids show this anxiety by throwing a fit or a tantrum. Sometimes parents don't recognize the reason for the tantrum- the child doesn't or can't appropriately express his feelings so they throw a fit.
Tip: Review and prepare. Show the child the website of where you are going (all attractions like museums, zoos, etc have websites with pictures), or show your child pictures of who you are visiting (grandparents for example). Discuss what you will do, what you will see, etc. Explain to the child it’s okay and normal to be a little anxious about doing something new or going somewhere new. Tell the child what the OK reaction should be. Also remind them how they can cope (hug parents, hold their hand, bring their favorite toy). Finally make sure you emphasize the fun part! Remind kids it will be fine.
Some kids do great with "Social Stories" where a story is written with the child in the story and it explains what will happen, what the expected behavior is, and reminds the child they are doing a great job learning whatever the skill is you want them to learn. (Search online for some free available social stories, or you can make one up yourself!)
Here's an example of something you can say to your anxious child before you go, and maybe during the car ride too. "I know sometimes you (or use "kids" in general if the child gets upset if you specifically focus on them) get a little worried or anxious when going somewhere new. It’s okay, and normal. Even mommies and daddies get anxious sometimes. (You can say if it’s true that you feel a little nervous too). Remember you can tell me "I feel worried" or "I'm scared" (use whatever feeling word you think your child is most familiar with and would understand) and come give me a hug, or you can hold my hand until you feel comfortable. We're going to do and see lots of fun things (give specific examples, if you can). I'm sure you will have lots of fun!”
(If you are leaving the child with a new babysitter for example, explain you will be back very soon and will give lots of hugs and kisses when you return, and you will miss them too.)
[see articles on breathing, preparing for a new school, separation anxiety and depression]

Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
ADHD- if you don’t think its “real” just ask a parent or teacher that has a child with this diagnosis! It can be so frustrating to work with a child with ADHD because they are usually a typical child with no delays or obvious special needs but yet they tend to lack focus, have to be told to do things that are a normal routine and they are usually unorganized and forgetful. Some kids are hyper and impulsive- sometimes in girls its hyperactive talkativeness instead of physical motor activity.
If you are seeing these symptoms have your child/student evaluated by a doctor or therapist and get some behavioral therapy. Some children may need medications (even some adults too!) but some may do fine with only behavioral interventions.
Some strategies to try to teach these skills:
· Fun focus activities: hidden pictures, mazes, word searches, etc (trains child to concentrate on something hidden which forces their brain to ignore the external stimuli/distractions)—can find lots of these for free online!
· Play Simon Says game to work on following directions
· Use reward system as kids with ADHD are often motivated by rewards!
· Do “following directions coloring pages” and activities- up to 3 step directions. For example: “color the tree orange, the flowers purple, and draw a sun in the sky”—this teaches child to remember 3 directions at once. Can use it for motor activities too like a game where you give directions and they have to try to remember all of it: “grab your jacket, two shoes, and put on your socks”.
Tiperoo: don’t give a child TOO many directions at once. If they are having a hard time just give them ONE at a time until they master that, then move on to about 3 directions at once.
· Make Checklists! Make one for morning routine, completing any task where they forget the steps -make a list and have them check it off daily! (can pair it with a reward chart). There are many free printable checklists online or you can make your own. Use this also for chores.
· Remove distractions, like the ipad, preferred toys, etc, from your child’s room/view in the morning. You can reward them with play time if they finish their morning routine tasks within enough time (show them a timer or clock). [See Morning routine section under Section 1]
· Use a Timer!! They are great to teach time management skills. You can download free visual timers on phones and ipads or order a ribbon timer or other visual timer from www.timetimer.com
Tiperoo: set a timer and have them “Beat the timer” as a competive game to teach them to move quicker through getting dressed, showering, etc
· Have them clear/clean out their backpack weekly- remove all old papers, re-organize current necessary papers. Perhaps eliminate multiple folders and keep everything in one large binder or one folder with multiple sections to make things simpler. Try color coding and clear labeling of where things go (can attach to a reward chart for keeping it organized)
· Clearly label and organize your child’s room/toy space for them and teach them to put things where they go (follow up weekly). For example bins/drawers for each clothing, toy, papers, etc.
Tiperoo: Take a photo of what the space or task should look like and then tell your child to make it look like the picture. For example their bedroom, desk, shoes/coat area, loaded dishwasher, toy bins, etc.
· Keep their homework work space clear of distractions (visual and audio) by keeping it quiet area, no TV in background or other people, toys, etc. Check in with child often to make sure they are on task and keep working. Timers and little reminder cards can be helpful to keep them on track too.
· Try a “keep working slider”. Put a button or bead on a pipe cleaner/string on a card and slide it along the card as your child completes their work so they can see their progress toward being finished. You can also do this with putting velcroed cards that say “start”, “middle” “end” etc or numbers 1-5 that you keep putting in a row to complete as they work so they can see their progress as well and know how much time is left to be done!
· Take movement breaks between things that require a long time of sitting such as walking around/jump on trampoline between homework subjects, classes at school, long car rides, sitting through church, a play, movies, etc.
· If your child is struggling in school ask the school to evaluate your child. Then request a 504 accommodation plan (this would include things like quiet space to take tests, teachers making sure they turn in their homework, extra time for assignments, sitting close to the teacher, etc) or IEP plan (includes goals for behavior and /or academics and may include specially designed instruction where teachers would have to tailor their approach to meet your child’s needs or may need to place child in a more appropriate classroom setting).

Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)
by Patience Domowski, LCSW
Oppositional Defiant Disorder, “ODD”, is a childhood behavioral disorder characterized by extreme defiance, opposition to adult authority, including angry mood, easily irritable, argumentative behavior, often vindictive- does things purposefully to annoy others or get back at others, refuses to comply with directions, blames other people for their own mistakes. These behaviors often occur across settings (home, school, and community), however sometimes it may only occur in one or two settings. It can occur from preschool ages through teen years.
Children with ODD often need a different parenting approach than their typical peers or siblings. They need a lot of structure. They need a very consistent and strict parenting approach. Instead of explaining why or giving reason for things, like might be helpful with other children, ODD kids need a simple, clear direction. They often don’t care about the why, they just want to argue and a logical explanation is not effective for these children. They need a regular routine, if possible. Knowing the expectation and what comes next can avoid a lot of problems.
Children with ODD need rewards and consequences. Often children with ODD and other behavioral disorders (such as ADHD) lack an internal feeling of happiness or pride in doing a good job, pleasing their parents or teachers, or feeling good about doing things they should do. They often need to be given a reason to motivate them to make a good choice or do what they are told because internally they don’t care. They often have that “what’s in it for me” attitude. If a child does not have an internal motivator, then they need an external motivator (reward) in order to comply.
They don’t need a bribe (giving them something first and expecting something in return) or a negotiation. They need simple direction and an opportunity to earn a reward. They also need clear (not vague) consequences for misbehavior. Use First/Then terms. First you have to do this behavior, then you can have/do what you want. Example: “First eat dinner, then you may watch TV”.
Use the word No sparingly. If it’s an absolute NO, use it. If it’s a “later”, use that term instead, as it may help avoid a tantrum from hearing the word No. They won’t be able to hear anything else after that word. Example: “You can play outside, as soon as your homework is done” instead of “No, you can’t go outside now”.
Use a reward chart system. Have the child earn rewards by doing certain behaviors – can be on a daily or weekly basis. There are many printable free reward charts online. A popular idea is the traffic light behavior chart where child is on “Green” for good listening, “yellow” for warning, and “red” for consequence.
Another similar (but non visual) strategy is 123 Magic, by Thomas Phelan. This is not the same as “counting to 3”. Basically the parent tells the child to do something and says “That’s one” along with the direction. If the child doesn’t behave after a reasonable wait time, the parent repeats the direction and adds “that’s two”. Again, the parent would wait, and if the child doesn’t follow the direction, the parent would say “that’s three” and immediately invoke a consequence. The consequence could be immediate or later, but the child would know at that moment that since they reached “3” they would get the consequence. However the direction still has to be followed.
Avoid empty threats. Don’t keep giving warnings and chances because the child will take advantage of that and try to manipulate parents to get their way and continue their behavior in order to get what they want.
Sticking to the consequence, providing rewards, and staying firm can go a long way in helping a child struggling with Oppositional Defiant Disorder. Seeking help from a behavioral therapist is helpful for the child to learn some strategies as well as helpful for parents to learn some different ways to handle their child’s behaviors.
Books by Patience Domowski, available on Amazon.com, print and Kindle versions
The (Un) Common Sense Guide to Parenting by Patience Domowski, LCSW
“Julian Learns” Series includes 3 stories in one book- stories include: “Julian’s Anger Story”, “Julian’s ODD behavior” and “Julian Learns Respect”. Book also includes reward chart ideas and worksheets for each story for child to practically apply their newly learned skills from the stories.

Emotionality and handling Meltdowns
When your child is very emotional/gets upset easily/meltdowns
Do’s and Don’ts for parents~ by Patience Domowski, LCSW
Do…
· allow your child to express their feelings (as long as they are safe)
· provide a safe spot for your child to go to calm down
· give your child space (if they are really angry don’t keep talking to them, let them calm down first or they will just get more upset)
· use a “code word” (silly secret word) for your child to say if they need space and need to be left alone when upset and respect that word by not continuing to engage with them at that time (Alternatively parents can use the word when they need child to give them space too to calm down)
· come up with a list of coping strategies/chill skills for child to use when child is in a good mood and post it where they can see it
· try to remind child of coping strategies BEFORE they become extremely angry (include an incentive like extra time with something or a treat if they use a chill skill to calm down)
· try to help our child recognize the middle part between annoyed and furious so they can work on calming at that time instead of when they are super angry
· wait until child is calm before problem solving
Remember: FIRST Calm, THEN problem solve!
Don’t…
· tell your child not to feel angry/anxious/sad/ etc (they can feel what they feel)
· punish your child for feeling [discipline for “behavior” not “feelings”]
· keep yelling/pushing your child to do what you asked/discuss the problem/etc when they are getting upset
· allow child to be disrespectful or aggressive even if they are upset. [If they do so have them apologize afterwards ]
· threaten things you don’t mean or won’t follow through with such as a punishment
· give in to child’s wants when they aren’t making a good choice, or after saying no already (even if it means a meltdown is coming)
I made this to attach pencil to desk for student who drops their pencil alot. ADHD kids tend to have their pencil fall off their desk several times a day !!

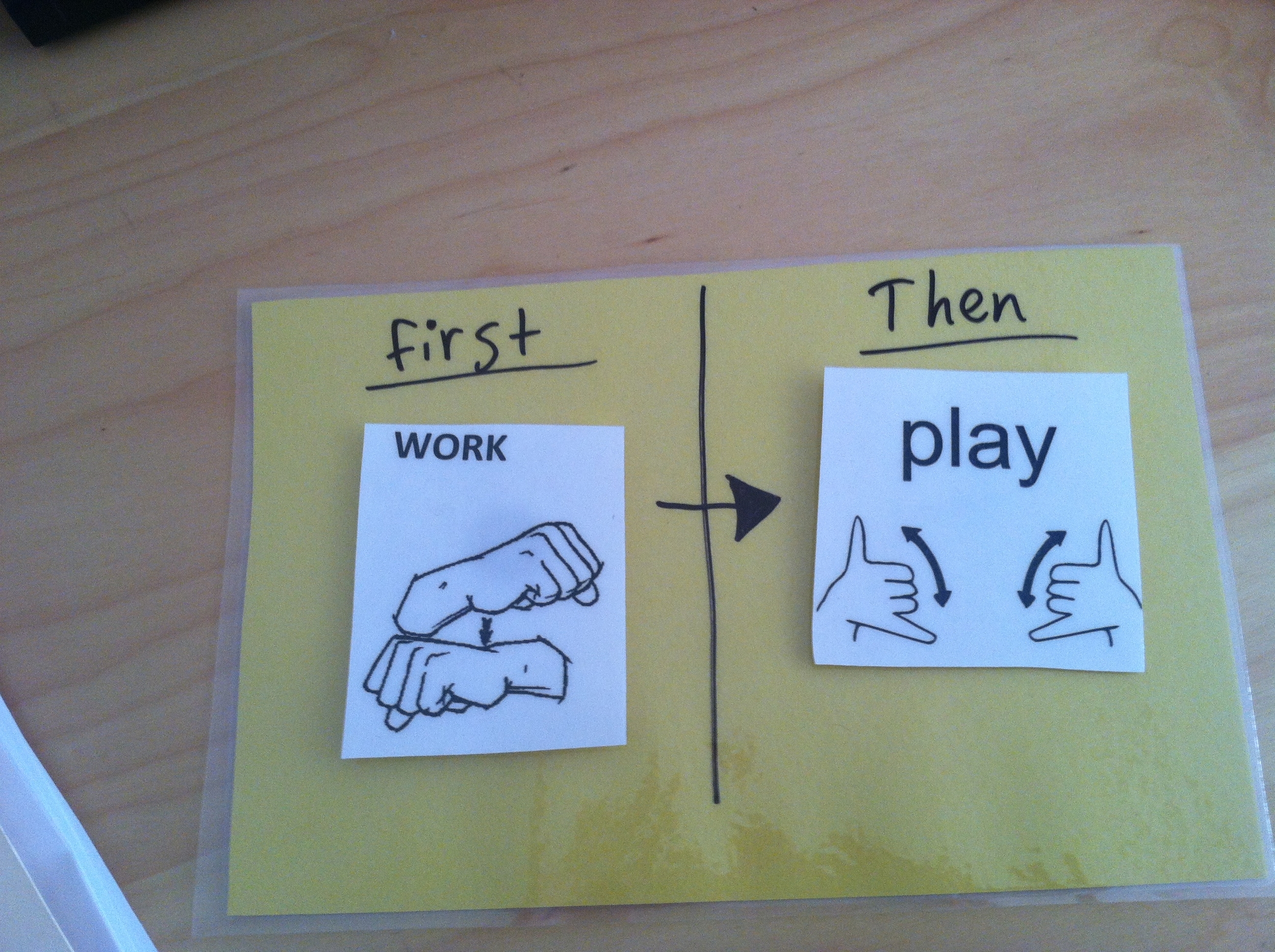
First/Then
This strategy is really helpful for kids with autism but it can work with anyone! You make a card with two sections and put a picture/or write what you want the child to do first, and then the second part is something the child prefers. This is used for work, play, eating, going places, etc!

Helping your child calm their anger ~ Strategies for parents
~ by, Patience Domowski, LCSW
· Remind your child it’s okay to be angry but they need to make good choices when angry
· Make a list with your child of anger coping strategies and post it somewhere easy to see in the home
· Model using anger calming strategies for your child and let them know you are using the strategy. (For example: “I am really angry right now that you colored on the walls. I am going to take some deep breaths to calm down.” or “I am really angry that you lied to me about your homework. I am going to go to my room to calm down and then we can talk about it later.”)
· Name your child’s anger so they can recognize how they feel and also empathize with them. Just acknowledging the feeling can be helpful. Then offer a solution, if possible. (For example: “You seem really angry. I know its upsetting when your brother doesn’t want to play with you. It’s okay to be upset. Let’s figure out what we can do instead!”)
· Notice what sets your child off and try to avoid it if possible. For example: If telling your child “No” makes them angry try saying “Yes, after_______” if they can have what they want after they finish something you want them to do (behavior, homework, chores, et)
· Notice when your child is starting to escalate and bring it to their attention that they should use a calming strategy or if you know a situation is about to occur during which your child is likely to be upset prepare them to use a proper coping skill beforehand (For example: “I have to tell you something that will probably make you mad, please try to make a good choice and take a deep breath and let’s figure it out. Okay here is the news…”)
· If your child needs time away to calm down- give them space instead of yelling at them. If you think it’s rude for them to walk away and if they cannot ask for space politely, try a “code word” which lets you both know you need some space to calm down. The word should be silly and respected if used.
· Try a simple reward to help give your child an incentive to use their calming strategies such as a piece of candy if they use a strategy, or they get out of the something if they calm down, for example
· Tell your child when they are calm we will discuss how to problem solve the situation
· Try not to give them attention for making poor choices but more attention when they make good choices. Praise your child for making a good choice by calming down and focus on that good choice versus the other angry behaviors

If your child comes home from school and won't talk about their day, here are some suggestions...
1) Don't let them get away with "I dont know" or a shrug when you ask them about it. Keep asking, or don't let them move on until they give a response. Often they just dont want to think about it or hope you will just let it go. Once they learn they have to respond with something, they usually will! If they need some time to decompress after they come home, try asking them about it at dinner or bedtime instead of right off the bus.
2) Suggest options for them to pick from: "Which special did you have today? Music or Art?" , or give more closed-ended questions to get them thinking more specifically. "Who did you sit with on the bus?" ," What did you play at recess?" "Tell me something new/funny/etc that happened today?" If they are in preschool, for example, and the teacher sends home a paper/note daily to tell parents about the child's day, use that as a jumping off point to discuss. "I see your teacher said you played with playdough today, tell me about that?" or "Oh you had gym today, what did you play in gym class?"
3) Everyone in the family has to share something about their day at dinner. With parents and older siblings modeling this, younger children will often soon learn how to join in. It just becomes the expectation to discuss. This could be done at bedtime alternatively.
4) Let the child draw a picture of something that happened that day, or write down a response if they are not verbal learners or have difficulty with communication (often this will work better with kids with Aspergers)
5) I made up a form that I have used with some clients to have them write a little something or draw something about their day. In therapy I have used "I don't know" tickets. I give the child 5 tickets for example in therapy and when I ask them questions if they say " I don't know" I take away a ticket. When they run out of tickets (may be for a few different questions, not all at once) then they have to respond. Kids usually catch on quick and don't want to lose the tickets so will answer! Even if the tickets don't mean anything! They also will often not need the tickets after a few sessions, because they learn that I won't just drop it and they get used to responding to me.
6) Consider that your child might legitimately not know due to memory issues, too young to process, or they can't think about what happens in different settings when not in that setting. Try suggestion number 2 above and if that's unsuccessful, they may just not be able to respond at this time (until they are older or more advanced in learning/cognitive skills).

"Error Correction" is an "in the moment" teaching opportunity.
Basically take the child back to where they made the error (physically) and "re-do" the behavior the correct way.
For example: You are holding child's hand walking in the store. The child suddenly runs off. You chase him down. Instead of just telling him "Don't do that again!" Take him back to where he started to run off and hold his hand and make him walk that same space.
Another example I can give from experience. I used to see a child for therapy in a daycare. When I would show up he would rolls his eyes and groan. I was teaching him social skills and that is not the proper way to greet anymore, especially an adult. So I said "Let's try that again" and I told him what the expected behavior was: "You should say "Hi Miss Patience!" when I arrive. So I went back out the door and came back, expecting him to use the right behavior. We practiced that awhile. Another client I had would stick out his tongue when I arrived. I tried the same thing. I would go back outside and re-knock on his door and have him greet me properly. After a few weeks of that (I only visited 1-2x/week) he now does it properly without having to "re-do" the greeting.
By redoing the behavior in the moment it helps the child learn "muscle memory" to remember what to do. Kids tend to learn better (and so do some adults!) from kinetic learning (using your body) more than just verbal learning. So acting out a behavior or role-playing a social scenario can teach the skill better than just lecturing or telling a child what to do next time without practicing it.

When disciplining a child the most important thing is that they LEARN THE LESSON, not receive the punishment. Does that make sense? Yes, they should receive a consequence, but we need to make sure they actually learned the lesson so they don't repeat the undesired behavior.
You also want to make sure the consequences make the most sense so that the lesson is learned.
Natural Consequences and Logical Consequences:
Natural Consequences are the BEST because they are most likely to happen and tend to teach the best lesson. Logical Consequences are consequences that make the most sense, sometimes based on what the natural consequence would be if allowed to happen.
Here's an example: If you leave your bike out in the rain, it will likely rust. (or get stolen!). So if your child doesn't put his/her bike away- they should lose the privilege of being able to ride their bike (for a day or week perhaps). Another example: if you are mean to the cat, the cat won't want anything to do with you. So if the child is teasing/hitting the pets, then maybe they can't play with them for a day. If the natural consequence does actually occur this can be a very good lesson for the child (or spouse!).
So try to make the "punishment fit the crime" as they say, if possible. Also check with the child to see if they learned the lesson. "So honey you can't play with your toys today because you didnt clean them up yesterday. I hope you make better choices tomorrow", or "So what did you learn from not being able to play with your friends today? Yes you need to play nicely with them if you want a play date."
When you can't use the above consequences: (and other info)
Apologies: If you give your child a consequence and they beg and plead saying they are sorry. You should NOT give in, however acknowledge they are sorry, but still give a consequence (after all if you were to do something wrong at work, you might say you are sorry but may still be put on probation. Or if you got a speeding ticket, you can apologize to the cop, but he will likely still give you that ticket!) "I'm glad you are sorry, but you still are getting a consequence".
Whining is an easy one to solve ....

Ignore whining. Say "I can only listen to your big girl/ boy voice". If child is having trouble re toning his request then model it for your child. Say the request for them to repeat. For example... "I want a drink please, mommy!" ( in a normal/ nice tone).
Also you can record your child's voice and play it for them. You could imitate them to show them how they sound. Another option - you can say one phrase in two tones and have child identify which sounds better. If they pick the whiny one then just use a whiny voice when talking to them all day and see if they call you on it!

Sometimes before setting up a whole behavior plan to deal with sudden increase in behaviors of a child you should check to see if there is anything in the child's environment or physical body that might be affecting them.
For example if suddenly they are really having alot of behavior problems you might check and see if they are sick or have an ear infection. That's sometimes a cause but the child can't or won't tell you how they feel, or they don't know what's going on with them.
Here are things to consider:
Noises (loud, strange, etc may bother kids)
Lights (too bright, hum loudly like ones in grocery stores/commercial buildings)
Need to use the bathroom (especially number 2....)
Hungry
Thirsty
Too Cold/Hot
Sick
Tired/Sleepy
Hurt/Headache/pain

Use of Rewards is extremely effective for kids, especially kids with Autism, ADHD, ODD (oppositional defiant disorder), and related issues.
Find out what motivates your child. Rewards should be very individualized, personalized, and will vary based on the child's interest, age, and availability.
Rewards do not always have to be something bought like new toys.
Rewards could be :
-extra time (like stay up late, extra time on computer/game, etc)
-extra attention (play a game with mom/dad, go out somewhere with parents, etc...)
-special choice (pick what's for dinner, pick the movie the family watches, etc)
-trip out (for ice cream, accompanying mom/dad anywhere, playground, out to eat, etc)
Ask the child what they would like to earn or work for, and then negotiate.
If the reward can match the behavior that's even better! Like if they get all their homework done early they get to play a game with mom/dad or read an extra story before bed. Or if they do their chores (like set the table for example) they can help mom make dinner, if they like).
Reward charts can be about one specific behavior you want to increase, or used for several behaviors. The amount of time it takes to fill the chart should vary. For young children it should be pretty easy and often to get rewards (daily, or several times per day for extreme behaviors you are trying to stop), for pre teen kids usually weekly works, for teens, it should take longer to get rewarded (rewards for teens might be getting or using a cell phone, access to the family car, going on a trip/school event, things like that.)
Reward charts are super easy to make, print out, or even buy. Here are some of my favorite sites to find pre-made reward charts...
Super nanny reward charts - info on how to make/use
Printable SuperNanny reward charts
Free printable reward charts
This site has alot of different types of charts
Chuck E Cheese Rewards - can't afford much? Use these Chuck E Cheese reward charts to get free tokens to play!
Types of reward charts:
Earn tokens/points/stickers to get to a goal (like need 10 stars to get reward)
Move along a track/up a chart/numbers to get to top/goal (move up from 1 to number 10 to earn reward)
Earn puzzle pieces to put entire puzzle together (earn the picture that is on the puzzle, or something else)
Opposite of a reward chart- a consequence chart could be losing tokens for misbehavior, or lose other things the child has/likes (take away a favorite toy, perhaps). I only suggest this method when you are trying to extinguish a behavior, not replace it with something else and rewards aren't working. Positive rewards are better, but you can try this strategy if that's not working or not possible with the type of behavior you are working on...
It's the "X" out the letters strategy.
For example a child keeps asking to go to the store when you already said No or Not now. Or a child keeps hitting or keeps doing something you want them to stop doing. A creative strategy I have used is to X out letters to something the child wants. For example I was working with a child who wanted to play with trains. I told him we have to do this and that first, then we can play trains. He kept asking me and I got really frustrated telling him same answer. So I wrote the word "TRAINS" on a white board, and told him every time he asks me I will X out a letter. If there are any letters left when we finish the work we were doing then we would play trains, if not, we wouldn't. After losing two letters, he got it and I never had a problem with that again! Another child I worked with wanted to go to the Pool but wasn't listening to what I was asking him to do- he kept screaming/making noises to be silly/clapping loudly for no reason, etc. So I drew 5 little pools on a paper, and I told him every time he does the screaming/misbehavior I would X out a pool. Once all the pools were gone, he couldn't go to the pool. He lost the pool one time (we used this method several times) and was usually pretty good after losing one X or two. Ive seen teachers use this method if the class is supposed to have a fun party and they are acting up that day (too excited or whatever). The teacher writes PARTY on the board, and every time the students are talking/not listening, etc she would X out a letter. They didnt want to lose that party so it was a good reminder to not get all the letters X'd out!
There are lots of ways to teach kids to focus. One is to use a Timer (you can use a kitchen timer, watch, phone, or timer app!). Have the child play with something (preferred) for 3-5 minutes. They can't switch activities until timer goes off. If they try to leave bring them back until the timer goes off. Then they can switch activities! You can also do various other table tasks in between taking breaks such as mazes, dot to dots, coloring, worksheets, puzzles, games, etc to work on focus. Do each activity for about 5-10 minutes (depending on child's age and ability) and then take a little break
Recommended apps: "Countdown", "VisTimerFree" for iphone.

You can buy timers specifically for teaching children with ADHD or learning needs at www.timetimer.com

If your child lies alot it can be counter productive to ask him "Did you do 'thus and so'?" and then when he says "no" you punish him for lying and he will never admit to the truth. Its often more helpful to just say "I saw you do (whatever it was), so your consequence is..." or "I heard you did..." and then give a consequence or warning. If you really don't know if the child did something or not it may be helpful to ask them, but kids who lie constantly when you (or another witness) KNOW they did it, its usually easier to just not give them even an opportunity for lying and just move to the consequence for the behavior.
(c) 2017 Patience's Behavior Therapy | All Rights Reserved
Website built by Creatively Innovative